A second-trimester screening ultrasound is done between the 16th week of pregnancy and the 22nd week of pregnancy. In pregnancies whose age has been determined well and it seems that they do not need amniocentesis, the examination at 20-22 weeks is the best condition for ultrasound screening in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Also, if the age of pregnancy is not well determined, early scanning is required to determine the exact age and anatomical examination. In Iran, it should be noted that if there is an anomaly that has a legal abortion approval, a legal doctor is needed to obtain a legal abortion license and before 18 weeks 6 days, so it is better to plan the time of the anomaly scan in a form so that if there is Anomaly leading to abortion, its diagnosis should be done before 18 weeks and 6 days.
If no anomaly is observed in the examination of the fetus, the time of performing the sonogram of the anomaly scan is at least 30 minutes, and if there is an anomaly in the fetus, the examination time is more than one hour depending on the type of anomaly. In the ultrasound anomaly scan, all organs and organs of the fetus are examined and measured in a comprehensive and specific way, and the measurements are compared with the reference tables to determine how the fetus grows and develops and whether it is standard or non-standard. Determine the development of the fetus.
It should be noted that about 40% of fetal anomalies cannot be detected in the second-trimester anomaly scan ultrasound, and it is necessary to check them in the third-trimester anomaly ultrasound scan, which is known as a Latonsetet anomaly scan, so one should not expect that all the anomalies of the fetus can be checked during the anomaly scan of the second trimester.
In the comprehensive ultrasound of the second trimester of pregnancy (anomaly scan), the following are checked:
- Examination of the central nervous system Included:
Examining the cerebellum, the space behind the cerebellum (Cisterna Magna), the lateral ventricles, the corpus callosum (Cavum Septum Pellucidum), the cerebral grooves, the Choroid Plexus, and the spine. In spine examination, anomalies such as neural tube defects (NTD), scoliosis, sacral agenesis, caudal regression, etc. can be examined.
- The facial examination includes:
Examination of the eyes, the lens of the eyes, the distance between the two eyes, examination and measurement of the nasal bone, examination of the lips and chin.
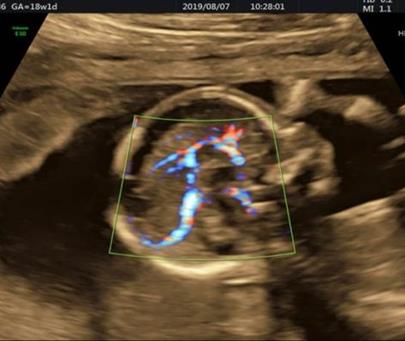
- Heart examination includes:
Examining the chambers of the heart including the atria and ventricles in the 4-chamber view, examining the large vessels of the heart such as the aorta and pulmonary arteries, examining the aortic and pulmonary arches, examining the valves, atria, ventricles, and the exit paths of the ventricles.
- Chest examination
- Examination of the lungs
- Examination of the abdomen (Abdomen) includes:
Examining the abdominal wall (in terms of examining the umbilical hernia) - Examining the diaphragms - Examining the stomach and intestines and examining the anatomical location of the stomach - Examining the kidneys and bladder. Anomalies of the urinary system include agenesis of the kidneys, polycystic kidneys, dysplasia of the kidneys, obstruction in the urinary system and simple cysts of the kidneys, etc., and about 57% of the anomalies of the urinary system are diagnosed before the 24th week of pregnancy.
Investigation of umbilical cord vessels.
- Examining the organs includes:
Examining the bones of the arm, forearm, thigh, and lower leg and examining the hands and soles, examining the axis and lower leg, and examining the fingers as much as possible. It should be noted that it is not possible to check the number of toes, especially in obese mothers. It is also not possible to check the adhesion of the toes.
- Examination of the uterine arteries:
Uterine arteries are examined without exception in all patients who refer to HopeGene Medical Institute. Examination of the uterine arteries in the first trimester of pregnancy to check for possible preeclampsia and examination of the above arteries at the time of abnormal scan (anomalous ultrasound in the second trimester of pregnancy) determines the state of blood supply from the mother to the fetus, and in case of a decrease in blood flow ( Flow) in the above arteries, it is recommended to perform color Doppler sonography of the uterine arteries in the 25th week of pregnancy.
- Examining the cervix, ovaries, and fluid volume around the fetus and placenta